Contents:
1. The Science of Solar Panel Efficiency
2. Absorption of Light: The Role of Color
3. Why Silicon-Based Solar Panels Are Black
4. Thermal Management: The Impact of Black Color
5. Black Solar Panels and Aesthetic Appeal
6. Solar Panel Color Variations and Market Choices
7. Solar Panel Types and Their Performance
Conclusion
Solar panels are an essential technology for harvesting solar energy, powering everything from residential homes to large industrial plants. Their design, materials, and functionality all work together to ensure that they are efficient and durable. One of the most noticeable features of solar panels is their color — most solar panels are black. But why is this the case? In this article, we’ll explore the reasons behind the color of solar panels, the science behind it, and how it affects their performance.

1. The Science of Solar Panel Efficiency
To understand why solar panels are black, we need to first grasp the principles of how solar panels work. Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) cells, convert sunlight into electricity. This is done through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes the solar cells, it excites electrons in the material (usually silicon), causing them to flow and generate an electric current.
The efficiency of a solar panel depends on several factors, including the material used, the quality of the components, and how much sunlight is absorbed by the panel. The color of the panel is directly related to how much light it absorbs and reflects.
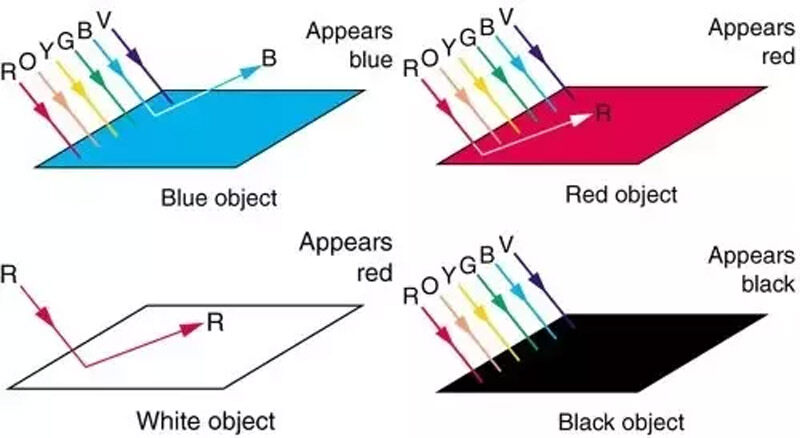
2. Absorption of Light: The Role of Color
Color is a reflection of how materials interact with light. When a material appears black, it is absorbing almost all of the light that hits it and reflecting very little. This is why many solar panels are black — the material used in these panels is designed to absorb as much light as possible, converting it into energy.
Black panels are made using a layer of silicon cells that absorb sunlight in the form of photons. The silicon cells are typically black due to their crystalline structure, which enables them to absorb more light and increase the overall efficiency of the solar panel. The more light a panel absorbs, the more energy it can produce.
3. Why Silicon-Based Solar Panels Are Black
The most common material used in solar panels is silicon, which is naturally dark in color. Silicon is used because it has the ideal properties for converting sunlight into electricity. There are two main types of silicon used in solar panels:

-
Monocrystalline Silicon: This type of silicon is made from a single crystal structure and has a dark appearance, making it ideal for efficient light absorption. Monocrystalline panels are often black because of the crystalline nature of silicon, which absorbs light very efficiently.
-
Polycrystalline Silicon: This type of silicon is made from multiple smaller crystals. It typically has a blue hue but is less efficient than monocrystalline silicon. While polycrystalline panels may appear blue or gray, they still absorb a significant amount of light but with lower efficiency compared to their monocrystalline counterparts.
Because black absorbs heat and energy efficiently, panels made from monocrystalline silicon are often black, ensuring the best possible performance.
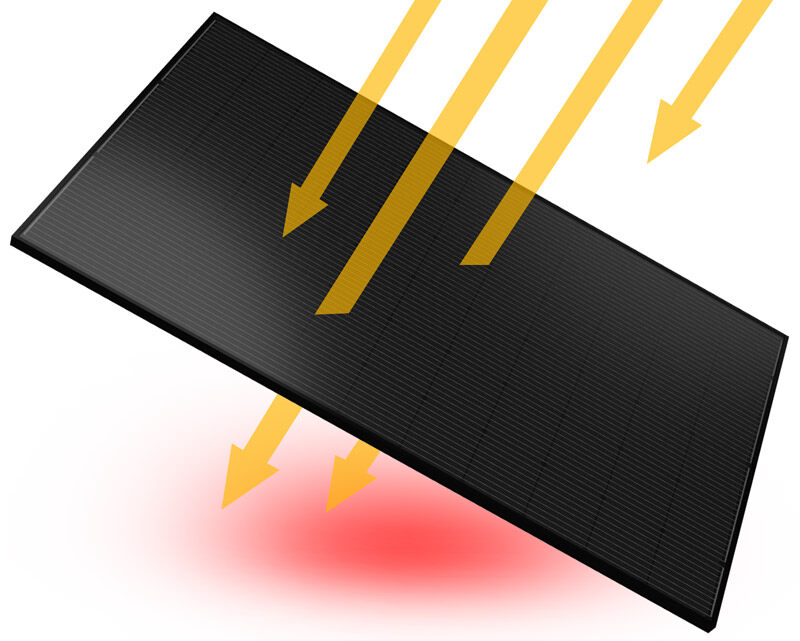
4. Thermal Management: The Impact of Black Color
One concern with black solar panels is the heat absorption. Since black panels absorb more sunlight, they also absorb more heat. Excessive heat can reduce the efficiency of solar cells by increasing the internal resistance of the panel. However, modern solar panels are designed with cooling systems and materials that help manage the heat and maintain optimal performance.
In fact, some solar panels have been engineered to cope with heat better than others. For example, certain black panels come with advanced heat-dissipation coatings that help cool the panel down, mitigating the risks of overheating. Furthermore, the black color tends to reduce the reflection of light from the panel's surface, which increases the amount of energy it absorbs, leading to better performance even in warmer climates.
5. Black Solar Panels and Aesthetic Appeal
Another reason black solar panels are commonly used is aesthetic. Black panels blend well with the roofing materials of most buildings, especially homes with dark-colored roofs. Their sleek, uniform appearance is more visually appealing to homeowners and businesses alike. Since the panels are often installed on roofs, the color choice is important to maintain a clean and professional look.
Additionally, black panels tend to look better in various lighting conditions. While they are more efficient in absorbing sunlight, their color also helps them blend in with the environment, making them less conspicuous when installed on residential or commercial buildings.
6. Solar Panel Color Variations and Market Choices
While black panels dominate the market, there are other colors available as well. Some manufacturers produce blue or gray panels, primarily made from polycrystalline silicon. These panels are typically less expensive but also less efficient in converting sunlight into energy.
There is also a growing trend of color-customized solar panels. Companies are experimenting with various coatings and designs to produce panels that blend seamlessly with architectural aesthetics. However, these panels often come with a performance trade-off, as color variations may reduce the amount of light absorbed.
7. Solar Panel Types and Their Performance
| Panel Type |
Color |
Efficiency |
Cost |
Lifespan |
Best For |
| Monocrystalline Silicon |
Black |
High (15-22%) |
High |
25+ years |
Residential and commercial |
| Polycrystalline Silicon |
Blue/Gray |
Medium (13-18%) |
Moderate |
25+ years |
Budget-friendly installations |
| Thin Film Panels |
Dark Gray/Black |
Low (10-12%) |
Low |
15-20 years |
Large-scale installations |
This table provides an overview of the different types of solar panels, their color, efficiency, lifespan, and best use cases. Monocrystalline silicon panels are often preferred for their high efficiency and aesthetic appeal, while polycrystalline panels offer a more affordable option.
Conclusion
The reason most solar panels are black is rooted in the science of light absorption and energy efficiency. Black panels made from monocrystalline silicon are particularly effective at capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity, making them the most efficient choice for solar energy systems. As technology advances, we may see even more color options emerge without sacrificing performance, but for now, black remains the preferred choice for both functionality and aesthetics in solar panels.









