Contents:
In the modern pursuit of sustainable development, renewable energy sources have become indispensable. Among them, wind and solar energy stand out as the most popular alternatives. However, a persistent question remains: Wind or solar energy, which is better? This debate continues to spark significant discussions, considering both environmental impacts and economic feasibility. To thoroughly answer this question, it's essential to examine their benefits, drawbacks, technological advancements, environmental implications, and economic aspects in detail.

Technological Aspects of Wind and Solar Energy
Wind Energy
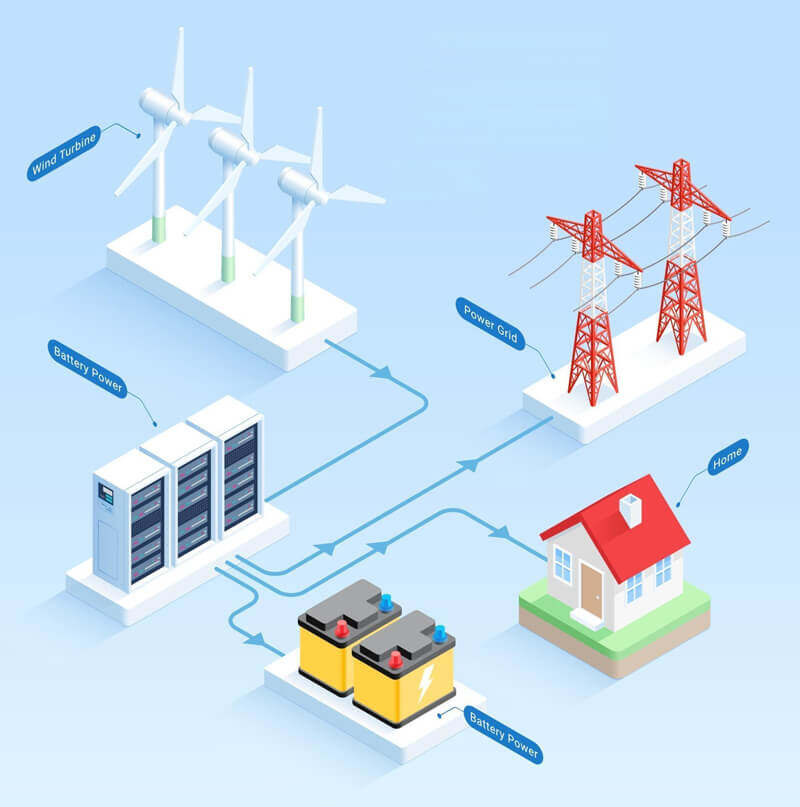

Wind energy harnesses the power of wind through wind turbines. These turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into mechanical energy, eventually generating electricity. Technologically mature, wind turbines have significantly evolved, becoming larger and more efficient over the decades.
One of the biggest advantages of wind energy is its capacity for large-scale power generation. Offshore wind farms, particularly in windy coastal regions, can provide massive amounts of energy without consuming substantial land areas.
Solar Energy
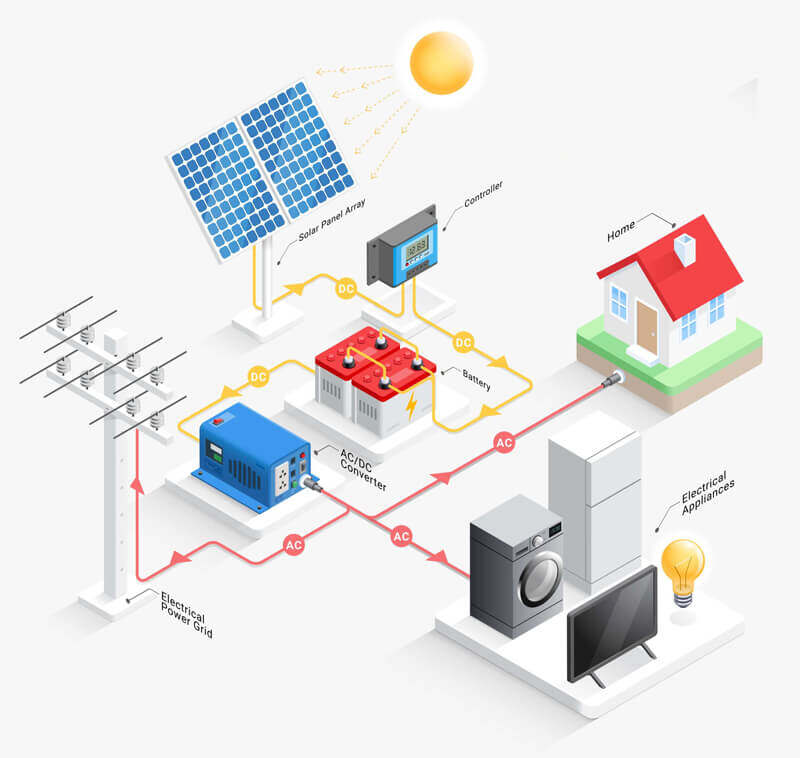
Solar energy, on the other hand, utilizes photovoltaic (PV) cells to convert sunlight directly into electricity. Solar technology is versatile, ranging from small residential panels to large solar power plants. Recent advancements in PV technology have led to increased efficiency and reduced costs, making solar energy highly attractive and accessible.
A critical advantage of solar power is its scalability and adaptability to various locations, particularly in regions with high solar irradiance.
Environmental Implications
Wind Energy
Wind energy is among the cleanest renewable energy sources, producing negligible greenhouse gas emissions during operation. However, environmental impacts such as noise pollution, visual disturbance, and effects on wildlife (particularly birds and bats) have raised concerns.
Solar Energy
Solar energy installations also present minimal emissions, significantly reducing the carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. However, the production and disposal of PV panels involve hazardous materials, posing potential environmental risks if not managed properly.
Economic Considerations
Initial and Operational Costs
Historically, wind power required substantial initial investment, primarily due to construction and installation expenses. However, technological improvements have significantly reduced these costs. Operational costs for wind turbines are relatively low, focusing primarily on maintenance.
Solar energy, despite high initial investments in PV panels, has seen a drastic decline in costs due to mass production and technological advancements. Its operational and maintenance costs are minimal, providing a strong economic case in the long term.
Subsidies and Incentives
Both wind and solar energies benefit from governmental subsidies and incentives aimed at encouraging renewable energy adoption. These subsidies significantly influence the economic attractiveness of both technologies.
Energy Generation Trends: Wind vs. Solar Energy (2015-2025)
The growth of wind and solar energy generation capacity worldwide provides clear insights into their respective development trajectories.
Line Chart: Global Installed Capacity of Wind and Solar Energy (GW)
(Data from 2015-2025, projected figures for 2024-2025)
Comparative Analysis of Wind and Solar Energy
Table: Comparative Analysis of Wind and Solar Energy
| Criteria |
Wind Energy |
Solar Energy |
| Efficiency |
35-45% depending on location and technology |
15-25% typical efficiency for photovoltaic cells |
| Environmental Impact |
Low emissions, noise pollution, bird collision risks |
Minimal emissions, hazardous materials in panel production |
| Installation Costs |
High initial setup, declining rapidly |
Moderate to high, significantly declining |
| Maintenance Costs |
Moderate, mechanical parts need regular upkeep |
Very low, minimal moving parts involved |
| Scalability |
Effective in large-scale setups, offshore expansion viable |
Highly scalable, suitable for diverse environments |
| Reliability |
Intermittent, dependent on wind consistency |
Intermittent, highly predictable sunlight patterns |
| Spatial Requirements |
Significant, especially for large installations |
Flexible, rooftop installations minimize land use |
Practical Applications and Suitability
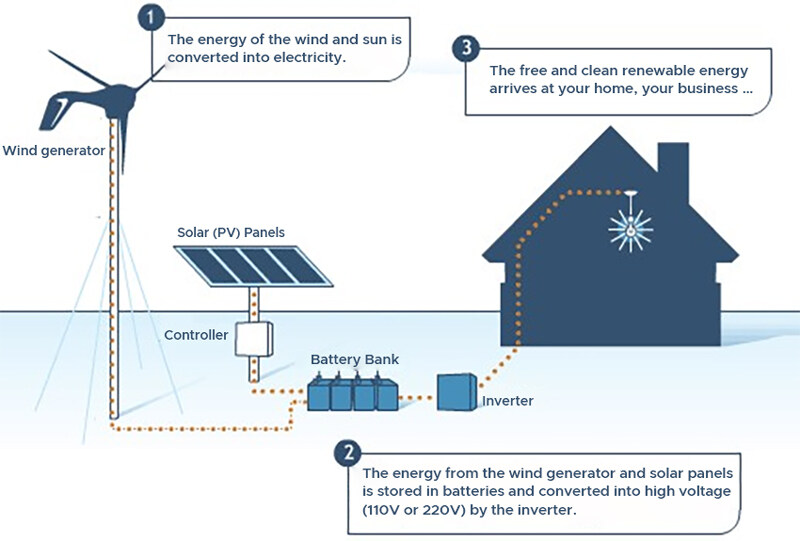
Wind energy suits areas with consistently strong winds, such as coastal regions and open plains. Its practicality increases with technological advancements like offshore wind farms, which can produce significant energy with limited spatial conflicts.
Solar energy thrives in regions with high solar irradiation, such as deserts and tropical areas. Its adaptability allows solar installations in diverse urban environments, including residential and commercial rooftops, thus reducing dependence on traditional power grids.
Conclusion: Wind or Solar Energy, Which is Better?
Determining whether wind or solar energy is better is context-dependent, influenced heavily by location, resource availability, economic factors, and specific use cases. Wind energy typically excels at large-scale deployments, especially offshore, benefiting from economies of scale. Solar energy, on the other hand, offers unparalleled flexibility and ease of integration into various environments, from residential rooftops to large-scale solar parks.
In conclusion, neither wind nor solar energy universally outweighs the other. Instead, the optimal approach involves strategically integrating both to harness their complementary advantages, ensuring a balanced, resilient, and sustainable energy future.
Ultimately, an integrated renewable energy strategy combining wind and solar energy will likely offer the best solution for achieving global energy sustainability goals.
1. What factors should I consider when choosing between wind and solar energy?
Consider geographic location, local weather, space availability, cost, government incentives, and long-term goals for sustainability.
2. Is wind or solar energy more cost-effective in the long term?
Solar energy tends to be more cost-effective for small-scale users due to lower maintenance, while wind is better for large-scale installations.
3. Which type of renewable energy is more reliable: wind or solar?
Solar is more predictable because of sunlight patterns, while wind can be more variable and less reliable without storage solutions.
4. What are the environmental drawbacks of wind and solar energy?
Wind can affect wildlife like birds and bats, while solar panel production involves hazardous chemicals and waste disposal issues.
5. Can wind and solar energy effectively replace fossil fuels entirely?
Yes, with energy storage, grid upgrades, and a diversified mix of renewables, wind and solar can significantly reduce fossil fuel dependency.









