As the global demand for renewable and sustainable energy grows, solar power continues to emerge as one of the most promising solutions. Derived directly from the sun, solar energy is abundant, clean, and increasingly cost-effective. However, “solar energy” is not a one-size-fits-all term—it actually encompasses several distinct types, each with unique characteristics, technologies, and applications.
In this article, we will explore the main types of solar energy, how they work, and where they are most effectively used.
_solar_energy.jpg)
1. Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy
How it works:
Photovoltaic solar energy is the most well-known and widely used type. It involves the conversion of sunlight directly into electricity using semiconducting materials—typically silicon-based solar cells. These solar cells are assembled into panels, which are then installed on rooftops, ground-mounted systems, or even integrated into windows and building facades.
Key Components:
Applications:
Advantages:
-
Easy to install and scale
-
Modular and adaptable
-
Increasingly cost-efficient
-
Works even in partial sunlight
.jpg)
2. Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
How it works:
CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area, generating high heat. This heat is then used to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to an electrical generator. Unlike PV systems, CSP converts sunlight into thermal energy first before turning it into electricity.
There are four main types of CSP systems:
Applications:
Advantages:
-
Thermal storage capability (can generate power after sunset)
-
High efficiency in direct sunlight
-
Ideal for utility-scale deployment

3. Passive Solar Energy
How it works:
Unlike PV or CSP, passive solar energy doesn’t involve mechanical systems. Instead, it refers to the design and orientation of buildings to naturally collect, store, and distribute solar heat. The goal is to reduce energy consumption for heating, cooling, and lighting.
Design Techniques:
-
South-facing windows (in the Northern Hemisphere)
-
Thermal mass materials (e.g., concrete, stone)
-
Insulation and glazing
-
Overhangs and shading devices
Applications:
-
Eco-friendly building designs
-
Residential and commercial construction
-
Retrofitting older buildings
Advantages:
-
No maintenance or energy input required
-
Significantly lowers heating and cooling costs
-
Environmentally friendly and sustainable

4. Solar Thermal Energy
How it works:
Solar thermal systems collect sunlight to heat a fluid, usually water or air. This heat can be used for domestic hot water, space heating, or even industrial processes. It's different from CSP because it’s typically used at a smaller scale and doesn’t generate electricity directly.
Types of Solar Thermal Systems:
Applications:
Advantages:
-
Cost-effective in sunny climates
-
Reduces reliance on gas or electric heating
-
Simple technology with low maintenance
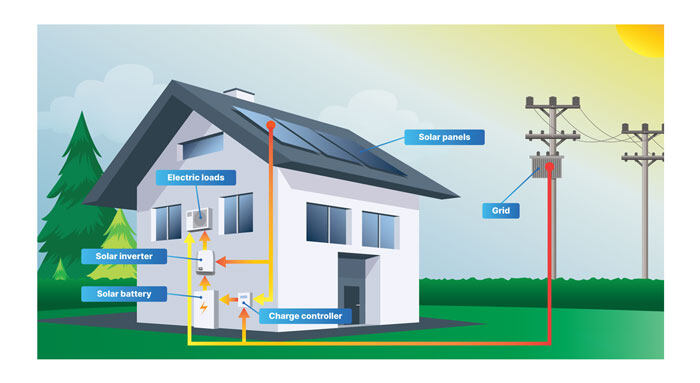
5. Hybrid Solar Energy Systems
What are they?
Hybrid systems combine solar with other energy sources or storage solutions, such as batteries or diesel generators. These setups are especially useful in off-grid locations or areas with unstable electricity supplies.
Types of Hybrid Systems:
-
Solar + Battery
-
Solar + Wind
-
Solar + Diesel Generator
Applications:
-
Remote or rural areas
-
Critical infrastructure (e.g., hospitals, telecom)
-
Residential backup systems
Advantages:
.jpg)
6. Floating Solar (Floatovoltaics)
How it works:
Floating solar power involves installing PV panels on floating structures in lakes, reservoirs, or water treatment facilities. This technology is gaining popularity in land-constrained regions.
Applications:
-
Hydroelectric reservoirs
-
Industrial ponds
-
Water treatment plants
Advantages:
Comparing the Different Types of Solar Energy
Here is a quick comparison:
| Type |
Electricity Generation |
Heat Usage |
Scale |
Best For |
| Photovoltaic (PV) |
✔️ |
❌ |
Small to large |
Homes, businesses, solar farms |
| Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) |
✔️ |
✔️ |
Large only |
Utility-scale power plants |
| Passive Solar |
❌ |
✔️ |
Building level |
Sustainable building design |
| Solar Thermal |
❌ |
✔️ |
Small to medium |
Water and space heating |
| Hybrid Systems |
✔️ |
Optional |
Variable |
Off-grid and backup systems |
| Floating Solar |
✔️ |
❌ |
Medium to large |
Water-covered areas |
Final Thoughts
Understanding the different types of solar energy is crucial for making informed decisions—whether you’re a homeowner looking to install solar panels or a policymaker developing a national energy strategy. Each type offers its own set of benefits and is suited to particular applications and environments.
While photovoltaic systems dominate the residential and commercial sectors due to their accessibility and falling prices, CSP plays a critical role in large-scale electricity production, especially in sun-rich regions. Passive solar and thermal systems support sustainability in construction and heating, while hybrid and floating solar technologies represent the innovation needed for expanding solar adoption in challenging areas.
As technology evolves, solar energy will become even more efficient, accessible, and vital to the global transition toward cleaner energy sources.
FAQs
What is the most common type of solar energy used today?+
Photovoltaic (PV) solar energy is the most widely used type, especially for residential and commercial electricity generation due to its affordability and scalability.
How does concentrated solar power differ from photovoltaic systems?+
Concentrated solar power (CSP) uses mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight and generate heat, which is then converted into electricity, whereas photovoltaic systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells.
Is passive solar energy really effective for reducing energy costs?+
Yes, passive solar design can significantly lower heating, cooling, and lighting costs by maximizing the use of natural sunlight without relying on electrical systems.
Can solar thermal systems generate electricity?+
No, standard solar thermal systems are designed to produce heat for domestic water, space heating, or industrial processes—not electricity. However, CSP systems do generate electricity using thermal processes.
Are floating solar panels more efficient than ground-mounted ones?+
Floating solar panels can be more efficient due to the cooling effect of water, which helps maintain lower panel temperatures and improves energy output, especially in hot climates.






_solar_energy.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)